目录
[TOC]
LLBT -> LLVM + Binary Translation
LLBT总体介绍——LLBT: An LLVM-based Static Binary Translator@2012
需要解决的问题
-
Code Discovery
ARM指令集和Thumb指令集,能确定是哪套指令集最好,不能确定则既按照ARM翻译也按照Thumb翻译。
-
Register Mapping
-
Instruction Translation
指令翻译分成3个部分,
- Conditional execution check
- Instruction body
- Conditional flags update
-
Handling Indirect Branches
建立原指令地址到目标指令地址的映射表。每当需要间接跳转时,就用原指令地址从这个表中查找目标指令的地址。因此一个简单的映射表会占很大的空间。
-
Jump Table Recovery
-
PC-relative Data Inlining
-
Helper Function Replacement
原指令集需要调用外部函数库(这里叫做helper function),比如没有浮点处理器,但是中间表示可以简单地表示出这些外部函数的功能。
st=>start: LLBT: An LLVM-based Static Binary Translator:>../../../Essays/BT/LLBT/2012.llbt.bor-yeh.cases.pdf
e=>end: A Retargetable Static Binary Translator for the ARM Architecture:>../../../Essays/BT/LLBT/2014.llbt.bor-yeh.taco.pdf
search=>operation: 在数据库中查找该作者写的其他引用率高的文章
test=>end: Automatic Validation for Static Binary Translation:>../../../Essays/BT/LLBT/2013.auto_validation.jiunn-yeu.applc.pdf
st->search->e(right)->test
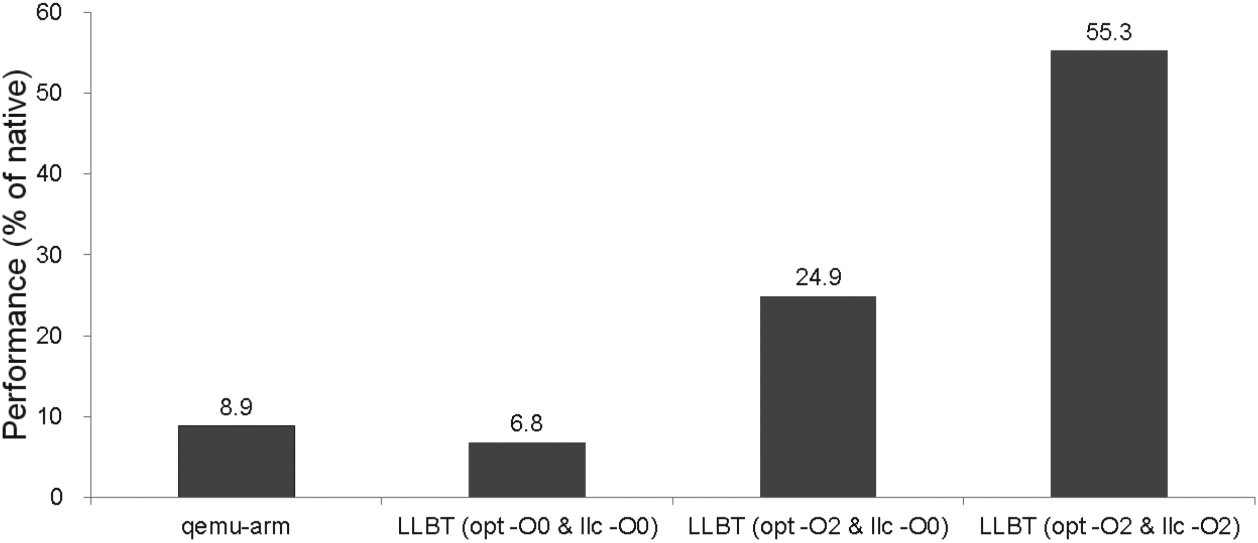
LLBT性能表现——A Retargetable Static Binary Translator for the ARM Architecture@2014
对LLBT正确性的自动验证——Automatic Validation for Static Binary Translation@2013
**感觉Instrunction Translation中提到的3点注意点和虚拟机的翻译并没什么太大区别。在这个地方可以一定程度的印证我的这个想法。**没有经过LLVM优化的代码的效率略低于QEMU的效率。
LLBT调研总结
🤔两个困难的问题:code discovery和code location。
🤓一个有趣的地方:为什么LLBT里还有自己的IR和自己的优化器?为什么不直接用LLBT的IR和优化器?
REV.NG
[A jump-target identification method for multi-architecturestatic binary translation](/home/xieby1/Zotero/storage/PCYM7WHA/Di Federico and Agosta - 2016 - A Jump-target Identification)@2016
这篇文章对上面的code discovery和code location问题有详细的举例说明。
🤔猜想&思考:为什么LLBT里还有自己的IR和自己的优化器?为什么不直接用LLBT的IR和优化器?
可能LLBT调用的是现有的虚拟机项目,比如QEMU。
将QEMU的IR转成LLVM IR 不用QEMU的IR而是直接生成LLVM IR 优势 可以“免费”享受QEMU开发者对QEMU的各种升级优化 创新的工作?翻译时间短。 劣势 市面已有类似的工作。翻译时间变长。 对QEMU源码进行阅读和修改,工作量大。需要自己维护自己的QEMU的版本。
🤓一个有趣的地方:为什么QEMU只能在同一操作系统间进行用户程序的模拟?
QEMU
Quick EMUlator
读音参考Wikipedia关于QEMU读音的讨论:👍Queue-Ee-Em-You
QEMU有自己定义的IR:(tb: translated block)
graph LR;
Binary-->QEMU_IR;
QEMU_IR-- 以tb为单位的opt -->QEMU_IR;
QEMU_IR-->Target
用命令查看源代码和QEMU生成的未经优化的IR的对比:
qemu-ARCH -d op DIR_TO_THE_BINARY
| 源代码 | 未优化的QEMU IR |
|---|---|
| .section .data output: .ascii "Hello World\n" .section .text .globl _start _start: | |
| ld_i32 tmp11,env,$0xfffffffffffffff0 movi_i32 tmp12,$0x0 brcond_i32 tmp11,tmp12,lt,$L0 | |
| movl $4, %eax | movi_i32 tmp0,$0x4 mov_i32 eax,tmp0 |
| movl $1, %ebx | movi_i32 tmp0,$0x1 mov_i32 ebx,tmp0 |
| movl $output, %ecx | movi_i32 tmp0,$0x8049096 mov_i32 ecx,tmp0 |
| movl $12, %edx | movi_i32 tmp0,$0xc mov_i32 edx,tmp0 |
| int $0x80 | movi_i32 tmp3,$0x8048088 st_i32 tmp3,env,$0x20 movi_i32 tmp11,$0x2 movi_i32 tmp12,$0x80 call raise_interrupt,$0x0,$0,env,tmp12,tmp11 set_label $L0 exit_tb $0x5597a136a043 |
| ld_i32 tmp11,env,$0xfffffffffffffff0 movi_i32 tmp12,$0x0 brcond_i32 tmp11,tmp12,lt,$L0 | |
| movl $1, %eax | movi_i32 tmp0,$0x1 mov_i32 eax,tmp0 |
| movl $0, %ebx | movi_i32 tmp0,$0x0 mov_i32 ebx,tmp0 |
| int $0x80 | movi_i32 tmp3,$0x8048094 st_i32 tmp3,env,$0x20 movi_i32 tmp11,$0x2 movi_i32 tmp12,$0x80 call raise_interrupt,$0x0,$0,env,tmp12,tmp11 set_label $L0 exit_tb $0x5597a136a183 |
QEMU-user
简介:QEMU有系统级模拟和用户级模拟。
- 系统级模拟需要下载系统镜像,需要设置硬件参数。能够模拟众多硬件架构(x86、ARM、MIPS…)、众多系统(BSD、Windows、Linux…)。
- 用户级模拟直接运行要模拟的程序即可。只能够在同一系统见进行模拟,比如可以在x86-Linux上模拟arm-Linux的用户程序,但是不能模拟x86-BSD系统。
QEMU
于是去阅读了QEMU-4.1.0(目前版本)的qemu-user的代码。总结出如下的结构图,